- 2-dimensional materials
- Synthesis of various 2D materials
-
-
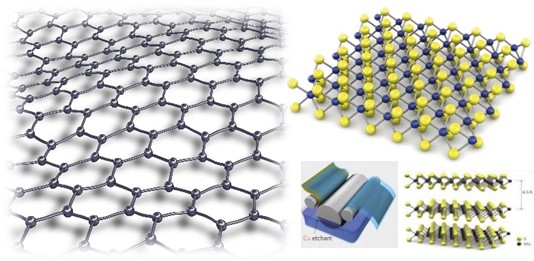
 For the last ten years, 2D materials emerged among many researchers headed by one
For the last ten years, 2D materials emerged among many researchers headed by one - atomic layer of graphite (graphene). We synthesized graphene and other 2D materials
- using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and solution-based process on various substrates.
- Our aim for the synthesis of 2D materials is large area and uniform synthesis of it.
- 2D material based ultra-thin heterogeneous devices
-
-
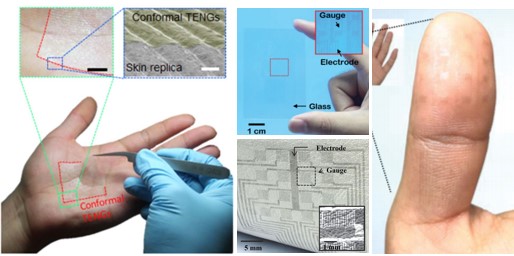
 The unique properties of 2D materials enable to demonstrate the various emerging
The unique properties of 2D materials enable to demonstrate the various emerging - applications such as wearable electronics, bio-engineering devices and human-machine
- interfaces. Our research in the 2D material-based electronics could inspire the development
- of the technologies of near future electronics.
- High performance flexible electronics
- Roll based transfer technique of inorganic thin-film
-
-
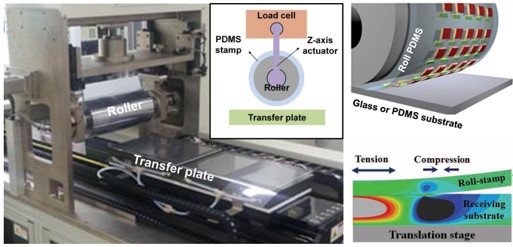
 Theroll-based transfer enables integration of heterogeneous thin film devices on aarbitrary
Theroll-based transfer enables integration of heterogeneous thin film devices on aarbitrary - substrate while preserving excellent electrical and opticalproperties of these devices,
- comparable to their bulk properties. Allroll-based transfer procedures could enable the high
- productivity and largearea scalability.
- Inorganic based high performance flexible / stretchable devices
-
-
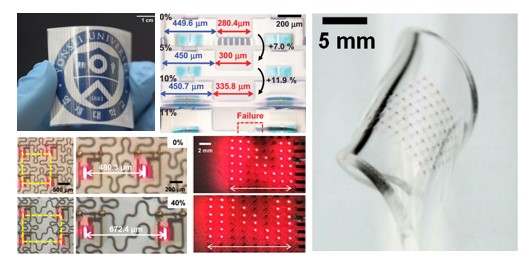
 Flexible/ stretchable electronics have led to promising classes of electronic device
Flexible/ stretchable electronics have led to promising classes of electronic device - applications such as tactile sensors for artificial electronic skins, wearableelectronic devices,
- stretchable displays, and electronic circuits.
Strain engineered electronic devices
-
-
-
New approach for strain engineering
-
-
-
-
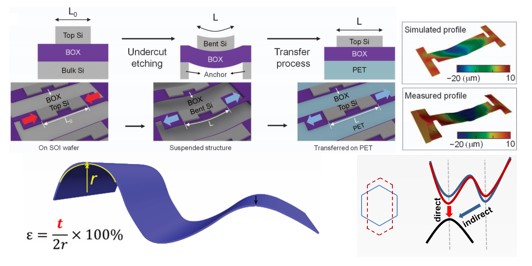
 Current strain engineering methods have several drawbacks: they generate atomic defects
Current strain engineering methods have several drawbacks: they generate atomic defects - in the interface between Si and strain inducers. We developed the formation of a strained
- semiconductor membrane with oxidation-induced residual strain by releasing a host mother
- substrate of wafer.
-
-
Device applications using strain engineering techinque
-
-
-
-
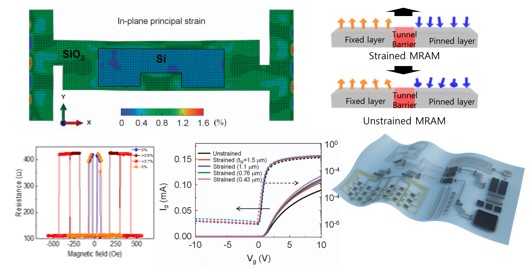
 We demonstrated the improved performance in the thin Si TFTs, MTJs on a flexible substrate
We demonstrated the improved performance in the thin Si TFTs, MTJs on a flexible substrate - by strain engineering without relying on the epitaxial stressor. This process can be applicable
- for various flexible electronic devices. This approach shows promise for strain-engineered
- large-area flexible electronics with high performance and productivity.


